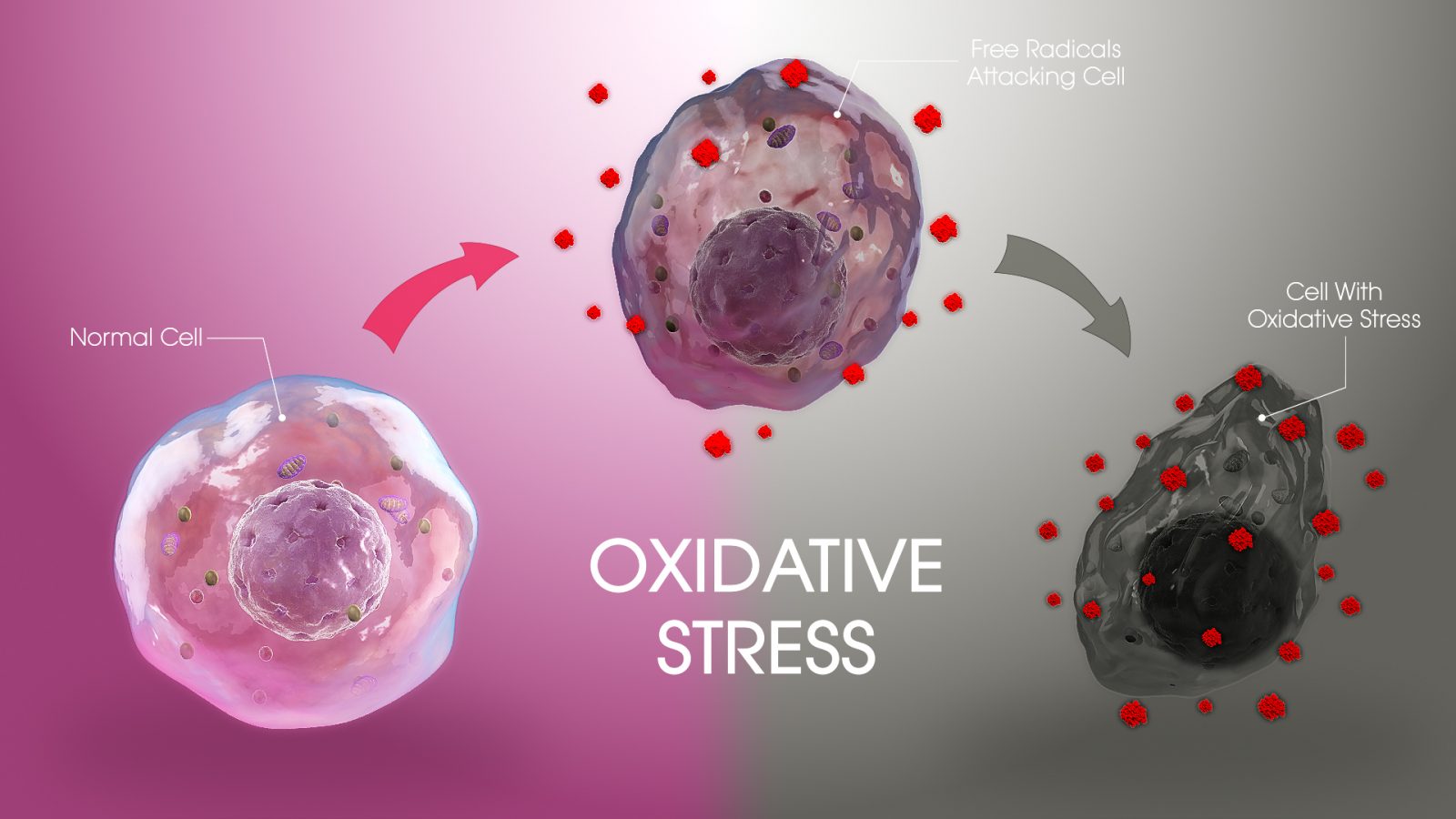
Oxidative stress causes cellular damage when there’s an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. While free radicals are naturally produced during normal metabolic processes like breathing, our modern environment and lifestyle significantly worsen the production of these harmful molecules. As we age, our body’s natural defense systems against free radicals, such as antioxidants, decline, making us more vulnerable to oxidative stress and its damaging effects. But what exactly are the main oxidative stress causes? Let’s dive into some key factors that contribute to this pervasive issue:
1. How EMF Radiation Affects Cellular Health
In our highly connected world, we’re surrounded by electromagnetic frequencies (EMFs) emitted from cell phones, tablets, laptops, WIFI routers, 4G/5G towers, and other wireless devices. While these devices have revolutionized the way we live, the constant exposure to EMF radiation can increase oxidative stress in the body. Research suggests that long-term exposure to EMF can generate free radicals, leading to cellular damage and impaired bodily functions【DoFollow link to possibilities to block】. Even the “blue light” from screens can disrupt our circadian rhythm, further contributing to oxidative stress.
 2. The Role of Diet
2. The Role of Diet
A diet high in processed foods, artificial additives, and sugars is another one of the major oxidative stress causes. Foods containing GMOs, gluten, artificial sweeteners, preservatives, and inflammatory ingredients like seed oils can lead to chronic inflammation, which in turn increases free radical production. Sugary foods, in particular, trigger insulin spikes that accelerate oxidative stress. On the flip side, a diet rich in antioxidants, like fruits and vegetables, helps to neutralize free radicals and minimize their impact【DoFollow link to read about a healthy diet】. Unfortunately, the standard modern diet lacks sufficient antioxidants, leaving our cells defenseless.
3. The Harmful Effects of Smoking and Alcohol on Your Cells
The harmful chemicals in cigarettes, including nicotine and carbon monoxide, promote the formation of free radicals. This not only damages lung tissue but also causes oxidative stress throughout the body. Alcohol, when consumed in excess, further adds to this burden. Even secondhand smoke and vaping can trigger oxidative stress【DoFollow link to study on smoking and oxidative stress】. For those who think switching to marijuana may be safer, it’s important to note that cannabis use can also impair cellular health by increasing oxidative damage.
4. Chemical Exposure: A Hidden Threat to Your Well-Being
The modern world is teeming with chemicals — many of which are untested for long-term safety. In fact, it is estimated that over 80,000 synthetic chemicals exist in our environment today, from household cleaning products to pesticides in food, and industrial pollutants in the air we breathe. This constant exposure overwhelms our body’s natural detoxification systems, leading to an accumulation of toxins and increased oxidative stress. Even seemingly innocuous products like shampoos, lotions, and plastics can contain harmful chemicals that disrupt our cellular balance. A friend of mine just had an allergic reaction to the new paint on her walls as there are preservatives in it.
5. The Link Between Obesity and Systemic Inflammation
Obesity is more than just a weight issue; it’s a significant driver of oxidative stress. The excessive fat stored in the body produces harmful substances called adipokines, which are hormones that cause systemic inflammation and oxidative stress. These adipokines can damage cells and tissues, leading to a range of health problems, from cardiovascular disease to insulin resistance. The chronic inflammation caused by obesity overwhelms the body’s ability to neutralize free radicals.
6. Why Chronic Stress is Damaging Your Body
Mental and emotional stress triggers a cascade of hormonal reactions in the body, releasing cortisol and other stress hormones that contribute to oxidative stress. This stress-induced hormonal imbalance accelerates aging, weakens the immune system, and promotes inflammation, all of which heighten free radical production. Chronic psychological stress also affects sleep patterns, immune function, and digestive health, creating a vicious cycle of cellular damage and oxidative imbalance【DoFollow link read more about resilience】.
 7. The Dangers of a Sedentary Lifestyle on Mitochondrial Health
7. The Dangers of a Sedentary Lifestyle on Mitochondrial Health
A lack of physical activity has been linked to numerous health problems, and oxidative stress is no exception. When we’re sedentary, the cardiovascular system doesn’t function optimally, leading to impaired blood circulation and mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondria are the powerhouses of cells, and when they’re not functioning properly, oxidative stress increases. Regular exercise helps reduce oxidative stress by improving mitochondrial function and boosting antioxidant production.
8. How Lack of Sleep Impairs Cellular Repair
Sleep is essential for the body’s repair and recovery processes. Without adequate sleep, the body struggles to heal and regenerate cells, leading to a buildup of free radicals. Chronic sleep deprivation weakens the immune system and promotes inflammation, both of which exacerbate oxidative stress. Studies show that poor sleep increases the risk of a wide range of health issues, including obesity, heart disease, and cognitive decline, all of which are tied to oxidative stress.
9. Understanding the Role of Illness in Glutathione Depletion
When the body is fighting off illness or infection, it requires more antioxidants to counteract the rise in free radicals. During illness, the body often experiences a decrease in glutathione, one of its most powerful antioxidants. This reduction impairs the body’s ability to neutralize free radicals, further contributing to oxidative stress. Even common ailments like the flu or a cold can increase oxidative stress, making it harder for the body to recover fully.
Conclusion: Reducing Oxidative Stress for Better Health
While it’s impossible to completely eliminate exposure to free radicals, there are steps we can take to minimize oxidative stress. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, eating an antioxidant-rich diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, and avoiding excessive exposure to harmful chemicals and radiation are all ways to reduce oxidative stress and improve your overall health. Your body is constantly fighting free radicals, and the best way to support it is by making conscious choices that enhance your natural defenses【Try Intelligent molecules, natures answer】.
With love and positivity,
Jennifer 🙏🏻💛